【文章摘要】Rural–urban fringe areas serve as crucial transitional zones within urban structures, and their spatiotemporal evolution holds significant reference value for scientifically planning urban configurations. The existing research predominantly focuses on large cities, overlooking the spatiotemporal evolution mechanisms of small- to medium-sized cities. This study employs nighttime light data as the data source to ensure continuous and consistent data, overcoming administrative boundaries. Taking Taizhou City as a case study, a combination of the threshold method and an improved Mann–Kendall algorithm is employed to reveal the evolution process of fringe areas. And a gravity model is utilized to unearth the interaction relationships among regions. The results indicate that from 2010 to 2020, the urban area expanded from 1097 km2 to 2791 km2, with fringe areas experiencing initial contraction followed by gradual expansion. The central urban areas of Jiaojiang, Luqiao, and Huangyan gradually merged, forming a concentrated region. Linhai maintained a high level of attraction, while spatial gravity weakened in other areas. This study quantitatively analyzes the expansion trends of fringe areas in small- to medium-sized cities, elucidating the attractive effects of time–cost distance and land resources on development and providing valuable support for subsequent spatial planning and governance.
【文章信息】Fu, B.; Xue, B. Temporal and Spatial Evolution Analysis and Correlation Measurement of Urban–Rural Fringes Based on Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16010088
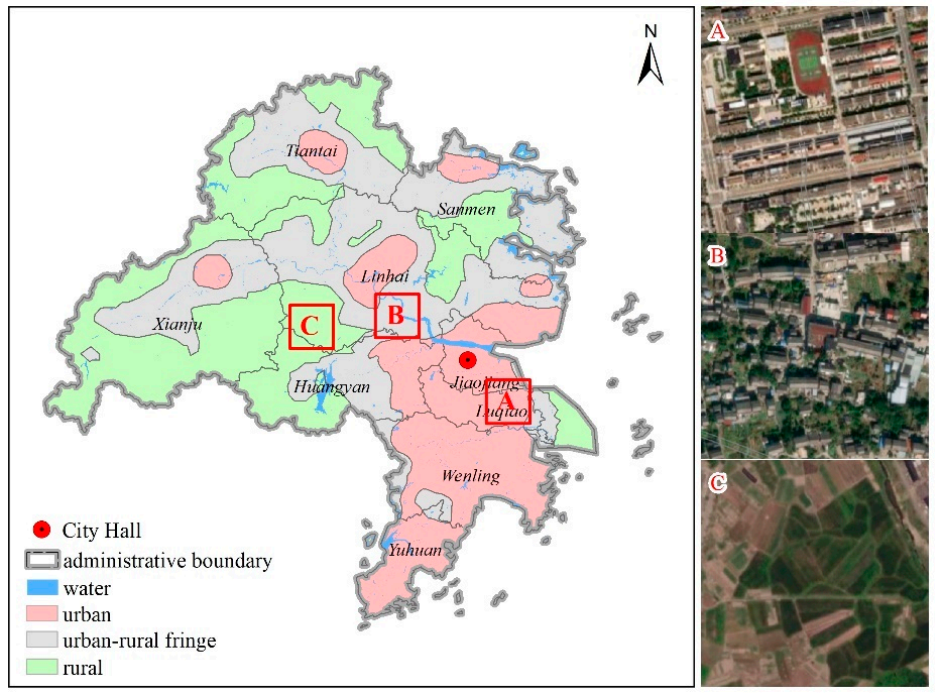
Comparative analysis of urban, urban–rural fringe, and rural areas in 2020 (A–C inquire about urban, urban rural fringe and rural validation areas, respectively).

