【文章摘要】Rooftop photovoltaic panels (RPVPs) implementation is one of the effective strategies to mitigate urban heat island and relieve urban energy demand with renewable energy resources, which is in need, especially during extreme heatwave events. However, the effects of RPVPs on cooling the urban thermal environment and saving energy have not been fully investigated in terms of RPVPs coverage (CV) and conversion efficiency (CE). To address this question, this study conducted a numerical evaluation of RPVPs on the thermal environment, cooling energy consumption (EC) in buildings, and electricity production (EP) during an extreme heatwave event in a semi-arid Chinese city using the WRF model coupled with building effects parameterization and building energy model. Simulations of twelve scenarios with four CVs and three CEs were conducted. The results indicated that RPVPs implementation could generally lower the 2-m air temperature, due to RPVPs’ higher effective albedo and higher emissivity. An increase in RPVPs CV and CE resulted in stronger cooling effects and larger cooling areas, where the RPVPs with a CV of 100 % and a CE of 0.3 could lower the 2-m air temperature by 0.4 – 0.7 °C, and significantly contributed to a decrease of cooling EC by 14.74 %. The EP could offset and even exceed the cooling EC, with the EP/EC reaching 182.61 %, 135.77 %, and 123.37 % in 100 % coverage (CE = 0.3), 75 % coverage (CE = 0.3) and 100 % coverage (CE = 0.2) scenarios, respectively, indicating that RPVPs could potentially generate enough electricity to compensate cooling EC in semi-arid cities. Our findings have practical implications for the RPVPs implementation and the necessity of improving conversion efficiency for better thermal and energy benefits.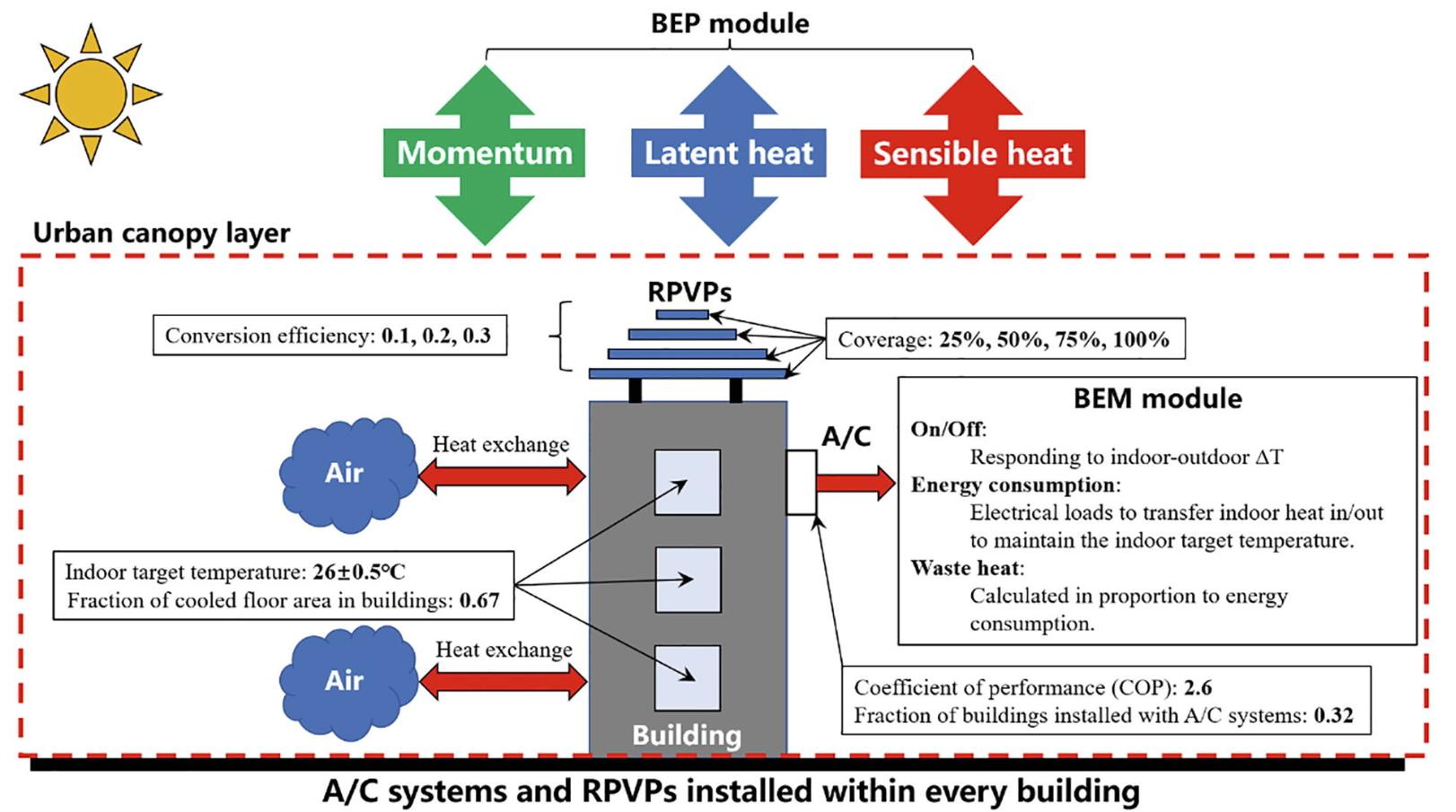
【文章信息】Shen, L D., Li, H D*., Guo, L C., He, B J., Thermal and energy benefits of rooftop photovoltaic panels in a semi-arid city during an extreme heatwave event[J]. Energy and Building, 2022, 275(15), 112490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.112490


